Nissan’s Tumultuous First Quarter: A Closer Look at the 2025 Financial Setback
It’s the story nobody at Nissan wanted to tell. Yet here we are: fresh numbers, hard truths, and very little sugar-coating. The Japanese automaker, Japan’s third-largest, if we’re keeping count, has racked up its fourth consecutive quarterly net loss. April through June 2025? Not great. Not at all. Net loss? A staggering ¥115.76 billion, or about $779.7 million, depending on the day’s exchange rate, numbers that sting, even for a corporation accustomed to rough roads.
But there’s more beneath the headlines. Nissan’s Q1 2025 story is one of changing times, international friction, and structural overhaul. Let’s get under the hood.
Q1 2025 by the Numbers
First, the cold, hard figures:
- Net loss: ¥115.76 billion ($779.7 million)
- Operating loss: ¥79.1 billion ($534.57 million)
- Consolidated net revenue: ¥2.7 trillion, down 9.7% from last year
- Global vehicle sales: 707,000 units
- Quarterly comparison: Last year’s April-June period netted a profit of ¥28.56 billion, so this year’s reversal is sharp
On some fronts, the pain was a touch less severe than analysts had braced for. But losses are losses, and they’re stacking up.
The Big Reasons Why: Tariffs, Restructuring, and Weak Demand
So, what’s driving Nissan deep into the red? Several factors, some years in the making, others “bolt from the blue” in style.
U.S. Tariffs: Costly Consequences
U.S. import tariffs hit Japanese automakers, Nissan perhaps hardest. These tariffs, aimed at shielding the American auto sector, have driven up costs just as Nissan was struggling to keep U.S. sales afloat.
- Direct financial bite: Nissan attributed a significant portion of its losses to these trade measures
- Wider market context: Japanese rivals like Toyota and Honda have also felt the pinch, but Nissan’s less-robust U.S. footprint has left it especially vulnerable
Slumping Global Demand, Especially in Key Markets
- United States & China: Traditionally lucrative, these markets saw weakened demand for Nissan vehicles, compounding the impact of tariffs
- Europe & Latin America: No safe harbors here, sales slumped, pulled down by an aging model lineup and tough competition
Massive Restructuring: Plant Closures, Job Cuts
If there’s a word for Nissan’s recent strategy, it’s “downsize.” Or maybe “survive.” The automaker’s global restructuring, ongoing for much of this decade, went into high gear this quarter.
- Plant closures: Nissan has committed to shuttering roughly seven factories worldwide over the coming years
- Mexico: Production at the Civac facility in Morelos will cease by March 2026, consolidating Mexican output at the Aguascalientes plant
- Japan: The Oppama plant will stop car production by March 2028; the Shonan factory lines will go quiet by March 2027
- Mexico: Production at the Civac facility in Morelos will cease by March 2026, consolidating Mexican output at the Aguascalientes plant
- Job cuts: Nissan’s strategy includes slashing 20,000 jobs by 2028, scaling back global production capacity from 3.5 million vehicles to about 2.5 million, excluding China
It’s a bold set of moves, sparked by years of declining market share and profitability. But the near-term cost is high: asset write-downs, redundancy expenses, brand disruption.
Inventory and Model Mix Problems
Don’t forget the “what’s actually on the lot.” Nissan’s current model mix, heavily reliant on aging offerings and slow-to-arrive EVs, hasn’t been enough to attract fresh buyers in North America or China.
A Closer Look: The Numbers, the Analysts, and the Peer Group
First, a funny thing: Nissan’s operating loss, bad as it is, beat the consensus forecast. Analysts polled by LSEG were bracing for a deeper cut, projecting an average operating loss of roughly ¥123.9 billion for the quarter. Nissan’s result, though grim, was “less bad” than feared.
And revenue? Down 9.7%, falling short of expectations. But here’s the kicker: These results still showed better operating discipline than in previous quarters. As CEO, Ivan Espinosa pointed out (if somewhat defensively), “We’re making strides in reducing expenses.” It’s not a victory lap, but maybe not as bleak as the numbers alone suggest.
Peer comparison? Toyota and Honda are still running rings around Nissan in global sales and profitability, with more successful hybrid and EV rollouts softening their blows from tariffs and a tough macro environment.
The Renault Factor
Oh, and then there’s Renault. Remember, Nissan is entwined with France’s Renault Group, which still holds a 35.71% stake in the company (direct and via trusts). Nissan’s losses are now weighing heavily on Renault’s quarterly results, too, a two-way street, with both automakers riding milestones and mishaps together.
- Renault’s estimated Q2 2025 income hit: -€127 million, thanks to Nissan’s poor performance
Restructuring: What’s Changing on the Ground
Here’s what Nissan is already doing and, if you squint, why it might matter by year’s end.
Shutting Plants, Shrinking Footprint
- Mexico’s Civac closure: Civil engineers and line workers alike saw this coming, with efficiency and localization as the official reasons. The Civac plant has produced 6.5 million vehicles since 1966; its end is an emotional blow
- Consolidation in Mexico: All Mexican Nissan vehicle manufacturing is shifting to the Aguascalientes complex
- Oppama and Shonan (Japan): Iconic but aging, these factories will wind down over the next several years. Their closure reflects Nissan’s move toward leaner, more modernized, fewer-but-bigger production sites
Job Cuts, Painful, Wide-Ranging
No glossing over it: About 20,000 positions are set to evaporate from Nissan’s global workforce by March 2028. These job cuts, announced as vital to restoring profitability, affect everyone from line laborers in Latin America to managers in Japan.
Manufacturing Capacity: Slashing to Survive
Nissan’s stated aim is to cut global annual vehicle manufacturing capacity by nearly 30%. Down to 2.5 million vehicles, with a reduced plant count: 10, down from 17. And, critically, excluding much of China’s unique operations.
How Did We Get Here? A Quick Recap
This is not all about 2025. Nissan’s woes have been several years in the making.
- Legacy of declining sales: Once a global upstart, Nissan lost ground in the U.S., Europe, and crucially, China, as rivals outpaced them in innovation and brand loyalty
- CEO scandals and management churn: Leadership instability sapped morale and investor confidence, just as the industry began a costly pivot to electrification and advanced tech
- COVID-19 ripple effects: Production disruptions, chip shortages, and supply-chain chaos hammered profitability
Nissan managed to return briefly to profit in fiscal 2023 and 2024, but found itself repeating a sad refrain by late 2024 and into 2025: Red ink, quarter after quarter.
What’s Next for Nissan? 2025 Outlook and Beyond
If you’re scanning for a glimmer of hope, here goes:
- Full-year forecasts, cautious: Nissan has not issued a fresh net profit outlook for fiscal 2025, but maintains a gloomy stance for the near term
- Projected first-half loss, FY net sales: Nissan anticipates an operating loss of ¥180 billion for the first half of 2025 and net sales of about ¥5.5 trillion
- Dividends on hold: The company confirmed it will pay no dividend for the year, bucking analyst expectations
Strategic Pivots: Electric Vehicles, New Alliances
Nissan’s long-term recovery hangs on its ability to compete in EVs, hybrids, and, yes, the “software-defined vehicle.” Investments in electrification are slowly ramping up, but rivals still lead, especially in China and Europe.
- Partnership programs: Nissan continues to lean on its alliance with Renault and Mitsubishi Motors for cost-sharing in technology and procurement
- Fresh models: A new generation of models, especially electrified ones, is expected to roll out in late 2025 and into 2026, but will it be soon enough?
Industry Context: Not Just a Nissan Problem
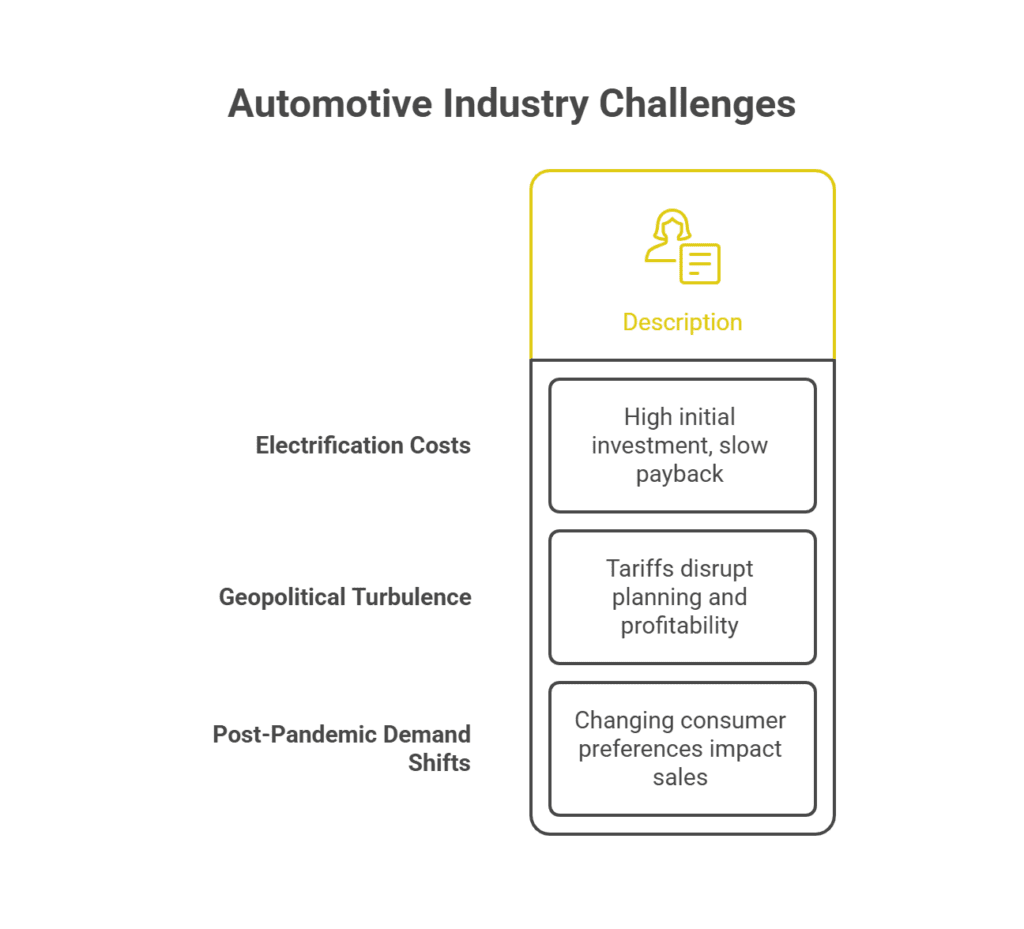
It’s only fair to note, Nissan isn’t alone in feeling the squeeze. Global automakers are weathering:
- Electrification costs: Research, development, and supply chain overhauls for EVs are expensive, with few models providing quick payback
- Geopolitical turbulence: Tariffs, particularly between China, the U.S., and Europe, disrupt planning and profitability
- Post-pandemic demand shifts: Consumer preferences are swinging, away from sedans, toward crossovers and SUVs, and toward brands with buzz
For Nissan, however, the margin for error is much thinner.
2025: The Road Ahead, Can Nissan Rebound?
Here’s where the story gets open-ended.
Nissan’s turnaround hinges on more than just cost cuts and closures. It needs revived market momentum in North America and China, successful launches in hybrid and EV segments, and a renewed sense of purpose. Not to mention, reconnecting with customers, many of whom have shifted loyalty over the last decade.
If I’m honest, it’s a steep climb. But this automaker has weathered crises before. The difference in 2025? The pace of industry change is faster, and the patience of investors and consumers, perhaps shorter.
Key Takeaways: A Snapshot of Nissan’s Q1 2025 Challenge
- Fourth straight quarterly net loss, driven by tariffs, restructuring, and sluggish global demand
- Job cuts, plant closures, and reduced global capacity dominate Nissan’s turnaround strategy
- Full-year outlook remains negative, reflecting ongoing market and operational pressures
- Longer-term recovery depends on successful electrification strategies and improved sales in the U.S., China, and beyond
- Nissan’s alliance with Renault/Mitsubishi remains both a lifeline and a source of added tension, as losses ripple through multiple companies
- The next moves, new model launches, global economic shifts, and industry trends will be watched by investors, workers, and car buyers alike
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Why did Nissan lose money in Q1 2025?
A mix of U.S. tariffs, falling sales in critical markets, and hefty restructuring costs, including closing plants and laying off workers, pushed Nissan deep into the red.
How is Nissan responding to its losses?
Through aggressive restructuring, shutting plants, slashing jobs, cutting global vehicle production, and consolidating manufacturing locations.
Are Nissan’s problems unique?
No. But its exposure to U.S. tariffs, a reliance on older vehicle models, and slower EV rollout leave it especially vulnerable compared to peers like Toyota and Honda.
What’s the outlook for the rest of 2025?
Not rosy. Nissan projects ongoing losses, holds dividends, and expects to work through more tough changes ahead.
Final Word
Nissan’s Q1 2025 report reads less like a footnote and more like a warning siren for the global auto sector. The pressure is on: from Wall Street, from workers, from buyers. The automaker’s next steps in cutting costs, revamping its model lineup, and restoring lost ground in vital markets will determine whether this year marks the bottom, or just another step down a long road.
Stay tuned, there’s plenty more to come out of Yokohama before the year is over.