The Keto Diet has taken the health and wellness world by storm, promising rapid weight loss, improved mental clarity, and better metabolic health. But what exactly is this diet, and does it live up to the hype? In this in-depth guide, we’ll explore the science behind the keto diet, its benefits and drawbacks, practical tips for success, and common myths. Whether you’re a newbie to keto or want to fine-tune your strategy, this article provides evidence-based guidance to help you make informed, data-driven choices.
The Keto Diet: How It Works
The ketogenic (keto) diet is a high-fat, low-carb eating regimen aimed at getting your body into a state of ketosis. Your body would normally run on glucose (from carbs) as its fuel source. When carb consumption is severely cut back (usually to 20–50 grams daily), the body starts to run on fat. The liver converts fats into ketones, which then serve as an alternative fuel source for the muscles and brain.
Key Principles of the Keto Diet:
- Low Carbs: 5–10% of daily calories from carbohydrates.
- High Fat: 70–80% of calories from healthy fats.
- Moderate Protein: 15–20% of calories from protein.
This macronutrient balance not only encourages fat burning but also maintains blood sugar and insulin levels within a healthy range.
Benefits of the Keto Diet
Scientific research and personal accounts point to several possible benefits of the keto diet:
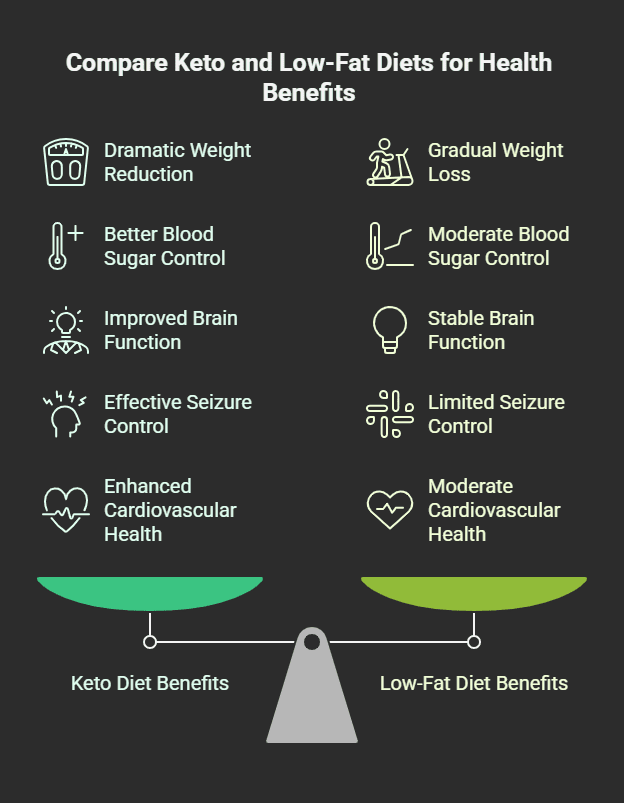
- Weight Loss: By reducing hunger and increasing fat burning, keto can result in dramatic weight reduction. A review of the British Journal of Nutrition in 2013 discovered that keto dieters lost more weight than low-fat dieters over six months.
- Better Blood Sugar Control: A study in Nutrition & Metabolism (2018) indicates that keto could lower HbA1c levels, which is helpful for those with type 2 diabetes or prediabetes.
- Improved Brain Function: Ketones are a productive fuel for the brain, possibly enhancing concentration and lessening brain fog.
- Seizure Control: First formulated in the 1920s as an epilepsy treatment, the keto diet is still a treatment for drug-resistant epilepsy.
- Cardiovascular Health: If executed well (focusing on unsaturated fats), keto can enhance HDL cholesterol and triglycerides.
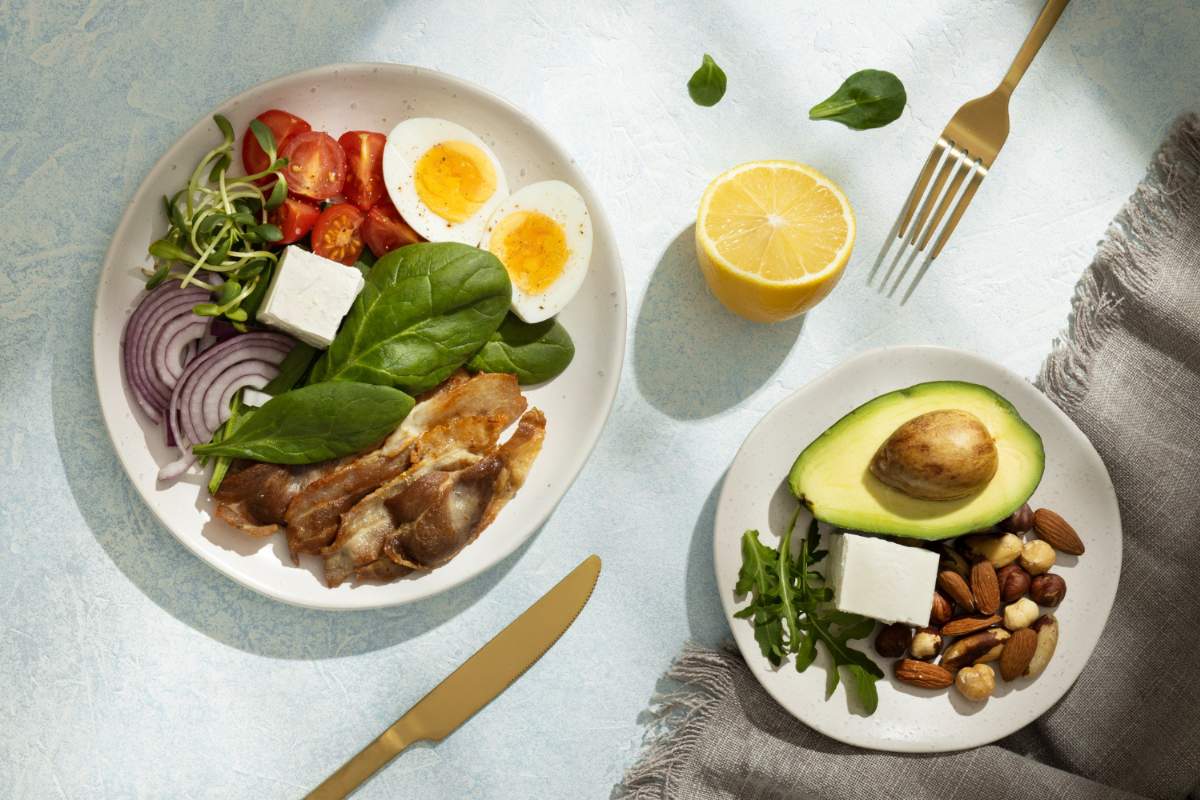
Foods to Enjoy on the Keto Diet
Structuring a keto plate involves strategically choosing nutrient-rich, low-carb foods
- Healthy Fats: Avocados, olive oil, coconut oil, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish such as salmon.
- Proteins: Grass-fed meats, poultry, eggs, and tofu.
- Low-Carb Vegetables: Spinach, kale, broccoli, cauliflower, and zucchini.
- Dairy: Full-fat cheese, butter, and unsweetened Greek yogurt.
- Beverages: Water, herbal tea, and black coffee.
Avoid: Sugary snacks, grains, legumes, starchy vegetables (potatoes, corn), and most fruits (except berries in small amounts).
Potential Side Effects and How to Manage Them
Switching to keto may produce short-term side effects, commonly referred to as the “keto flu”:
- Fatigue
- Headaches
- Nausea
- Constipation
Solutions:
- Hydrate and replenish electrolytes (sodium, potassium, magnesium).
- Taper off carbs gradually rather than an immediate change.
- Add fiber-rich, low-carb vegetables to facilitate digestion.
Most symptoms disappear within a week as the body adjusts.
7 Tips for Being Successful on the Keto Diet
- Plan Meals: Pre-cook keto essentials such as cauliflower rice or grilled chicken.
- Monitor Macros: MyFitnessPal-type apps enable monitoring of carb consumption.
- Experiment with Recipes: Experiment with keto pancakes (almond flour + eggs) or zucchini noodles.
- Watch for Hidden Carbs: Read labels for sugars in sauces, dressings, and processed foods.
- Get Moving: Exercise speeds up ketone production and burning fat.
- Sleep Well: Poor sleep disrupts ketosis and heightens cravings.
- Consult an Expert: A nutritionist can make the diet specific to you.
Debunking Common Keto Myths
- “Keto Means Eating Unlimited Bacon”: Although keto is fat-heavy, quality is more important. Use avocados and nuts instead of processed meats
- Keto is Unsustainable.”: Most use cyclical keto (5–6 keto days with 1–2 higher-carb days) to maintain long-term compliance.
- “Keto Causes Muscle Loss”: Proper protein intake maintains muscle mass, particularly when combined with strength training.
The Science Behind the Keto Diet
Recent research supports its effectiveness:
- A 2020 meta-analysis in Obesity Reviews upheld keto’s advantage over low-fat diets for short-term weight loss.
- Cell (2017) research associated ketosis with less inflammation and a longer lifespan in mice.
Long-term effects (more than 2 years) are still poorly researched.
Who Should Not Follow the Keto Diet?
Safe for the majority, keto is not ideal for
- Pregnant or lactating women.
- People with pancreatitis, liver disease, or unusual metabolic disorders.
- Those with a history of eating disorders.
Always consult a medical professional before beginning.
Conclusion
The keto diet presents an intriguing solution to weight loss and metabolic wellness, supported by developing research. But success depends on careful food choices, adequate planning, and attention to your body. By recognizing the benefits and pitfalls, you can determine whether keto is a good fit for your lifestyle and objectives. Remember, there is no one-size-fits-all approach—balance and sustainability are the keys to long-term health.