OpenAI’s GPT-4.1 Model Family: Expanding the Boundaries of Niche Artificial Intelligence
OpenAI has just rolled out its GPT-4.1 family, comprising GPT-4.1, GPT-4.1 mini, and GPT-4.1 nano. Its new set of large language models is an expansion of GPT-4o, with improvements in coding, better instruction following, and increased context window. These models are only accessible on the OpenAI API, targeting enterprise users and developers.
The “4.1” naming, rather than a straightforward numerical upgrade, reflects emphasis on improving current capabilities. The concurrent retirement of GPT-4.5 implies strategic realignment, perhaps for reasons of performance or economics. The coding and API-only emphasis reflects a keen interest in the developer market.
Core Features and Technical Specifications of GPT-4.1 Models
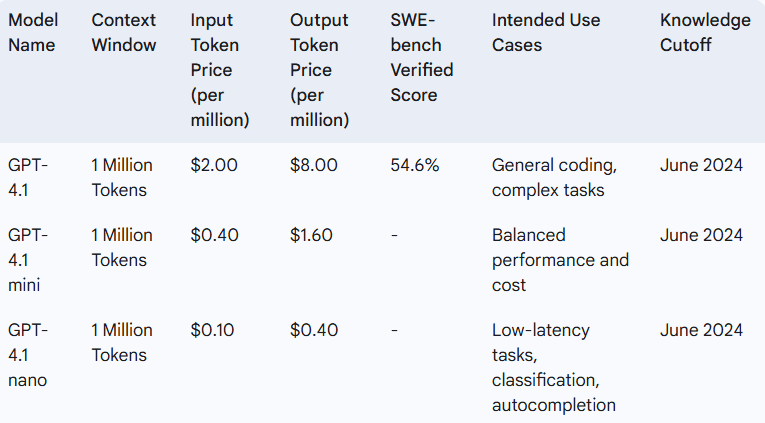
GPT-4.1 has three models:
- GPT-4.1: The general coding and heavy task flagship model.
- GPT-4.1 mini: Balanced performance and affordability, said to outperform GPT-4o in most benchmarks with lower latency and cost.
- GPT-4.1 nano: The most efficient and lowest-latency, optimized for low-latency applications such as classification and autocompletion.
GPT-4.1 scores 54.6% on the SWE-bench Verified benchmark, a substantial improvement over GPT-4o (33.2%) and GPT-4.5 (approximately 28%). It also surpasses GPT-4o in code diff generation, front-end web app development, following output formats, and reducing unnecessary edits. Yet, its SWE-bench score remains less than Google’s Gemini 2.5 Pro (63.8%) and Anthropic’s Claude 3.7 Sonnet (62.3%).
All three models share an increased context window of one million tokens, significantly more than GPT-4o’s 128,000. This enables them to handle longer codebases and documents with greater accuracy.
GPT-4.1 also demonstrates improvements in compliance with complex instructions, at 10.5 percentage points better than GPT-4o on the MultiChallenge benchmark. They are more consistent in following output formats and less likely to make unnecessary changes.
The pricing structure is tiered:
- GPT-4.1: $2 per million input tokens / $8 per million output tokens.
- GPT-4.1 mini: $0.40 per million input tokens / $1.60 per million output tokens.
- GPT-4.1 nano: $0.10 per million input tokens / $0.40 per million output tokens.
GPT-4.1 is reportedly 26% less expensive than GPT-4o for typical queries. The discount for prompt caching has also increased to 75%. The knowledge cutoff date for all models is June 2024
Significance of Enhanced Coding Abilities
Enhanced coding proficiency in models such as GPT-4.1 facilitates code generation, bug finding, and support for software workflows, possibly enhancing developer productivity and development time. LLMs are “code interpreters,” which render coding easier and enable quicker prototyping. They do automate a lot, yet human knowledge continues to be necessary for complicated projects. Code-based training can also improve reasoning capacity in other areas. Products such as GitHub Copilot already capitalize on these advancements.
The improved coding capability of GPT-4.1 marks the way towards more trustworthy AI-powered development tools, which could further enhance AI dependency in the software development process. Strategic thinking and problem-solving abilities of human developers, though, are still required for complex projects. Competition from tools such as Gemini 2.5 Pro and Claude 3.7 Sonnet requires a solid assessment based on the requirements of the particular project.
Implications of the Extended Context Window
The one-million-token context window enables GPT-4.1 models to digest and comprehend enormously more amounts of information, so that better summarization of documents, answering of questions, comprehension of code, and general-purpose reasoning is made possible. The capability of AI agents is further boosted since models can have longer-term context-maintenance over their interactions. But models could fail with data located in the center of very lengthy inputs (“lost in the middle”). Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has the potential to augment large context windows by concentrating the model on the most context-specific information. This enhanced ability may change domains such as legal and scientific studies and software coding, but further research is required to streamline information processing over such extended contexts.
Competitive Landscape: GPT-4.1 vs. Other Top AI Models
Google’s Gemini 2.5 Pro, with an equally sized context window and expansion plans underway, is a significant challenger. It frequently bests GPT-4.1 in coding metrics, which makes it a good fit for coding-oriented tasks. Anthropic’s Claude 3.7 Sonnet also has good coding output and a 200,000-token context window. GPT-4.1 demonstrates multimedia data comprehension strengths. The competitive landscape entails ongoing innovation, which means developers must compare models on a case-by-case basis, taking performance, cost, and features into account.
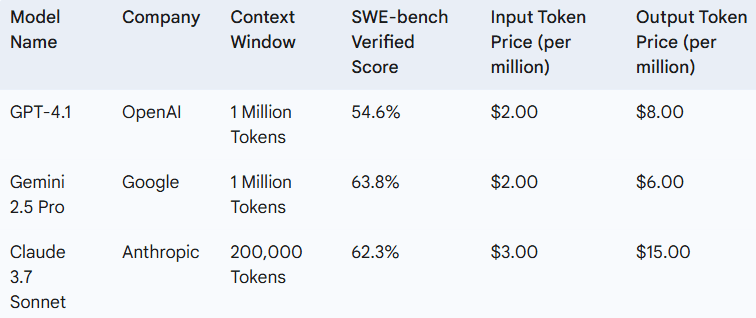
Note: Pricing for Gemini 2.5 Pro is based on estimations. Claude 3.7 Sonnet pricing is for the Sonnet model.
The Retirement of GPT-4.5 and the Future Outlook
OpenAI will sunset GPT-4.5 API access by July 14, 2025. GPT-4.1 is comparable or better and at a lower price point, making GPT-4.5 less important. OpenAI CEO Sam Altman has teased more models in the future, such as o3 and o4-mini, with an emphasis on reasoning power. OpenAI’s approach seems to be moving in the direction of single-purpose models instead of working towards a single general-purpose model such as GPT-5 in the immediate future.
Conclusion:
GPT-4.1: An Important Leap Forward in Expert AI
The GPT-4.1 model family signifies a major development in specialized AI with enhancements in coding, instruction following, and the window size of context. These developments place GPT-4.1 as a suitable tool for developers, even within the competitive marketplace. OpenAI’s prioritization of specialized models and cost makes it a demonstration of ongoing efforts to address changing needs in the AI space.