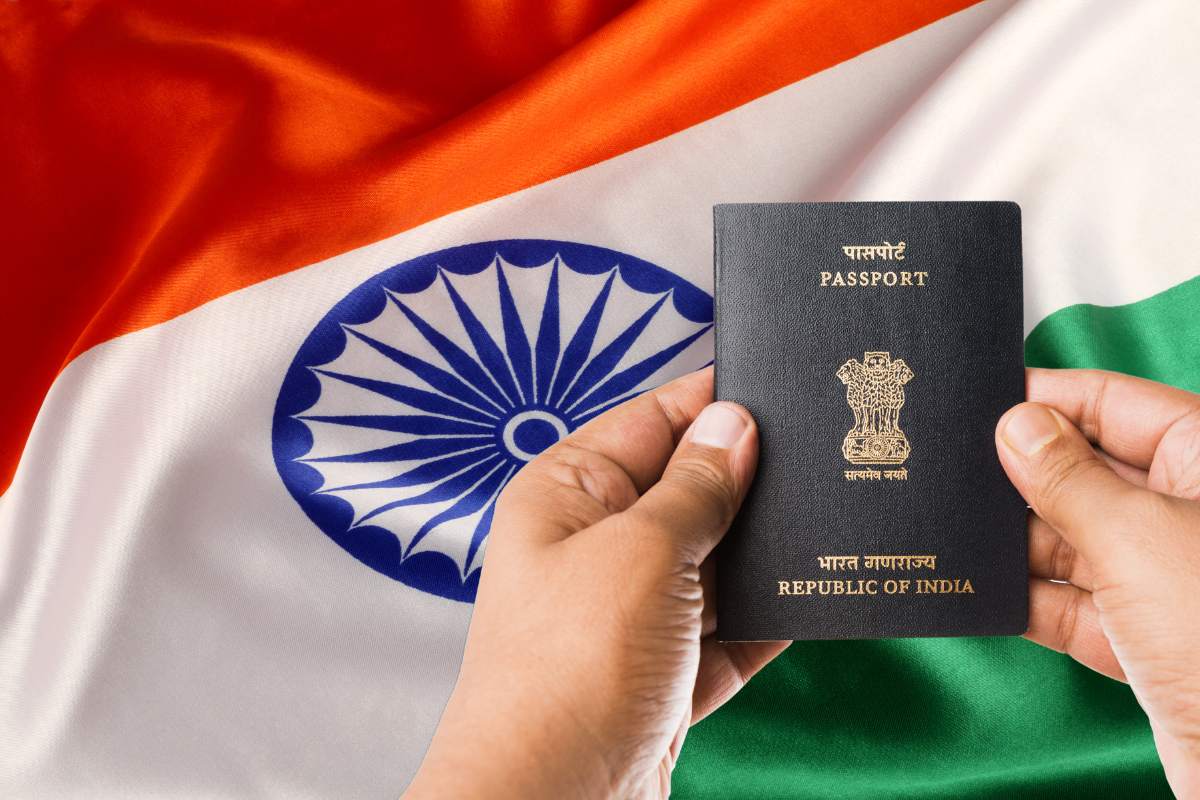
India has formally begun the issuance of its cutting-edge travel document, the India e-passport, as part of its bold passport system modernization. The document combines the traditional paper booklet with cutting-edge electronic technology, ensuring greater security and an easier traveling experience for citizens. The move, in equal measures tradition and innovation, seeks to redefine global travel for Indian citizens. This detailed manual will delve into the technology used in these Indian e-passports, their many advantages, the step-by-step method of applying for them, the status of their implementation in the nation, and where they stand globally in terms of travel documentation. Learning about the Technology:
What is an E-Passport?
An Indian e-passport, or simply called a biometric passport or chip-based passport, maintains the look of a traditional passport but carries high-tech electronic features.
The central part of this technology is an embedded Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) chip and an antenna, unobtrusively mounted inside the back cover of the passport. This chip serves as a safe repository for the passport holder’s information, duplicating the details printed on the data page of the passport, along with biometric information. Such biometric information generally consists of an electronic photograph and fingerprint data. Although reports show promise of iris scans being used in e-passports worldwide, the rollout currently underway of India e-passports incorporates facial recognition and fingerprints for biometric validation in the majority of reports. A clear visual indicator differentiates the Indian e-passport from its conventional counterpart: a small gold symbol printed immediately below the front cover. This symbol is an immediate cue that the RFID chip is embedded in it.
Key Features and Benefits of India’s E-Passports
The emergence of India’s e-passports highlights a plethora of benefits, all centered on greater security and easier travel procedures.
Increased Security via Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)
The Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) technology integrated into the chip is a pillar of the security design of the Indian e-passport. This advanced encryption and digital signature system is of crucial importance in protecting the contents of the chip, rendering it highly resistant to tampering, forgery, and identity theft. The continuous deployment of PKI throughout the development of India’s e-passports highlights its intrinsic role in creating a secure and reliable digital identity for overseas travel, according to international standards of data protection.
Accelerated Immigration Procedures with Automated E-Gates
Beneficiaries of India e-passports are anticipated to enjoy streamlined immigration procedures at airports that have automated e-gates capable of biometric passport verification. By opening access to these automated corridors, the India e-passport is designed to accelerate the clearance process significantly and minimize the need for manual checks by immigration staff, eventually resulting in reduced queues and a better experience for passengers. This benefit is specifically important in the current scenario of rising global travel traffic, where wait times at immigration points need to be kept to a minimum to improve the overall experience.
Global Compliance and Recognition
The chip embedded inside the Indian e-passport has been designed to meet international standards and adheres to the requirements of the International Civil Aviation Organisation (ICAO) standards. Such compatibility with international standards guarantees that India’s e-passports are universally accepted and can be easily authenticated by customs officials globally, thus lessening the chances of travel inconvenience or issues due to passport authenticity.
Data Tampering Protection, Forgery, and Identity Theft Protection.
The built-in design of the Indian e-passport, featuring the embedded chip and PKI-based security, provides strong protection against several kinds of fraudulent practices. The encryption of the data contained on the chip makes it much more difficult to counterfeit or alter than paper-based passports. This strongly mitigates the risk of identity theft and counterfeit passport circulation, leading to a more secure environment for world travel.
Double Data Storage: Printed and Digitally Signed
The Indian e-passport utilizes a dual storage approach, with the holder’s data existing in the old printed form on the booklet pages and also as digitally signed information within the electronic chip. Such redundancy not only provides an added layer of protection but also makes the passport usable even where electronic chip readers are not present.
Who Can Take Advantage? Benefits for Travelers
India’s e-passports bring numerous real advantages to travelers, improving their global travel experience.
Faster Immigration Processing and Smaller Wait Times
One of the strongest benefits for visitors who possess an Indian e-passport is the possibility of speedier immigration processing. By allowing automated lane usage at airports with biometric recognition technology, India’s e-passports can save considerable time in immigration queues. This is a direct response to one of the greatest issues facing overseas travelers, with the promise of a less troublesome and less time-wasting arrival and departure experience.
Convenience of Utilizing Automated Lanes at Airports with Biometric Verification Support
The fact that the Indian e-passport is digital makes it easy for travelers to use automated e-gates at airports that are equipped with the capability of supporting biometric passport verification. The self-service method simplifies the verification of identity, diminishing the requirement for immediate contact with immigration officers in most situations and making transit through airports smoother.
Enhanced Security and Less Risk of Counterfeit Activities
For tourists, India’s e-passports’ higher security features mean less risk of having problems arising from passport fraud or identity theft while travelling abroad. The high level of security contained in the Indian e-passport means that its holder has a higher level of security and trust associated with it.
How to Apply for an Indian E-Passport: A Step-by-Step Process
The application procedure for an Indian e-passport follows that of a standard passport to provide the applicant with a known process.
- Registration: The initial step is registering on the official Passport Seva Portal.
- Login: After registering, one must log in to the portal with their registered ID and password.
- Application Type: The applicants then choose the suitable application type, picking either “Fresh Passport” for new applicants or “Re-issue of Passport” for renewal of an already issued passport.
- Fee Payment: The applicable application fee is to be paid online using one of the payment options listed on the portal. The compulsory online payment for scheduling an appointment simplifies the process.
- Appointment Scheduling: Once payment is made successfully, applicants can book an appointment at a Passport Seva Kendra (PSK) or Regional Passport Office (RPO) of choice.
- Appointment Confirmation: At the time of booking, applicants must preserve the appointment confirmation, either by printing the application receipt or retaining the SMS confirmation sent to the registered mobile number. A printed copy of the application receipt is no longer required.
- Visit to PSK/RPO: On the mentioned date and time, candidates are required to report to the chosen PSK or RPO, bringing all original documents necessary for verification.
- Biometric Data Submission: At the time of appointment, candidates will be required to submit their biometric information, including fingerprints and a photograph, for registration in the system.
- Passport Delivery: After successful verification and processing of the application, the new India e-passport will be printed and sent to the registered address of the applicant.
The focus on online registration and appointment booking is a continuation of the drive to digitalize government services in India, offering a more transparent and convenient process for citizens.
Current Rollout Status and Availability
The issuance of India e-passports was initially started as a pilot project on April 1, 2024, simultaneously with the launch of Passport Seva Programme (PSP) Version 2.0. Issuance of e-passports was initially restricted to some regional Passport Offices. India e-passports are currently issued at the following centers: Nagpur, Bhubaneswar, Jammu, Goa, Shimla, Raipur, Amritsar, Jaipur, Chennai, Hyderabad, Surat, Ranchi, and Delhi. This phased roll-out implies a strategic rollout, possibly depending on the technical preparedness and infrastructure facilities of various passport offices. The Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) has made arrangements to bring the availability of India e-passports to all Passport Seva Kendras (PSKs) across the country by mid-2025.
It must be emphasized that moving to an e-passport is still not obligatory. 4 All current traditional passports produced by the government of India shall be valid until their respective expiry dates, ensuring a voluntary and gradual move towards India e-passports.
E-Passports vs. Traditional Passports: A Comparative Look
To better understand the advantages of India’s e-passports, a comparison with traditional passports is provided below:
| Feature | Traditional Passport | E-Passport |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Paper booklet | Booklet with embedded RFID chip and antenna |
| Data Storage | Printed only | Printed and encrypted digital chip |
| Security Level | Lower, prone to forgery | Higher, with advanced encryption |
| Biometric Data | Not included | Fingerprints and facial recognition |
| Immigration Processing | Manual verification | Electronic, faster verification |
| Global Acceptance | Based on country agreements | ICAO compliant, widely accepted |
| Risk of Forgery | Higher | Significantly lower |
India’s E-Passport in the Global Context
India’s move to introduce e-passports makes it part of more than 120 countries across the world that have already embraced this technology, including leading nations such as the United States, Canada, France, Japan, and Australia. Such extensive use is in itself a reflection of international acceptance of e-passports as the new frontier for secure international travel documents. By conforming to the standards presented in the International Civil Aviation Organisation (ICAO) Document 9303, India’s e-passports provide interoperability and worldwide acceptance. This step reflects India’s dedication to joining the worldwide initiative of improving travel security and efficiency, which is poised to lead to more convenient and easier travel experiences for Indians traveling overseas.
The Future of Travel with E-Passports
India’s e-passports have been seen as a first step towards a more inclusive digitalization of the travel environment in India. The government foresees future developments that will further optimize international travel. These are some of the possible developments that range from introducing mobile passport wallets, blockchain-based identity verification systems, greater integration with present digital ecosystems such as Aadhaar and DigiLocker, to even getting visas embedded onto the chip of the passports. The eventual destination of all these developments is to step towards a paperless, fully digital, contactless, and smart travel experience for everyone. This future-oriented perspective implies that the Indian e-passport is not so much an improved version of a physical passport but a building block in a larger digital identity system for future travel.
Conclusion
The issue of India’ e-passports is an important step towards the modernization of India’s passport regime and its pledge to increase the security and ease of international travel for Indian citizens. With their enhanced security features, such as the embedded RFID chip and PKI technology, and the potential for quicker immigration through automated e-gates, Indian e-passports are expected to provide a more secure, convenient, and hassle-free international travel experience for Indian citizens. Meta Description: Discover the new India e-passports, their latest features such as RFID chips and increased security, the advantages for tourists such as quick immigration, and an easy guide on how to apply.